AMR
Targets and Results
Medium- and Long-Term Targets
SHIONOGI aims to ensure that all manufacturing processes for antibiotics handled by SHIONOGI obtain the international certification “BSI Kitemark™ for Minimized Risk of AMR” from the British Standards Institution (BSI) by fiscal year 2035. Through third-party evaluation, this initiative is intended to objectively guarantee that antibiotics are manufactured responsibly with consideration for AMR occurrence and to clearly demonstrate this to stakeholders.
Furthermore, to reduce the environmental impact during the manufacturing process of antibiotics, SHIONOGI conducts audits (AMR audits) and provides feedback to its own group factories and suppliers (Table 1) that handle antibiotics and their drug substances/intermediates, aiming to achieve proper management of antibiotic environmental emissions throughout the supply chain.
Initiatives for AMR
Acquisition of BSI Kitemark™ for Minimized Risk of AMR Certification
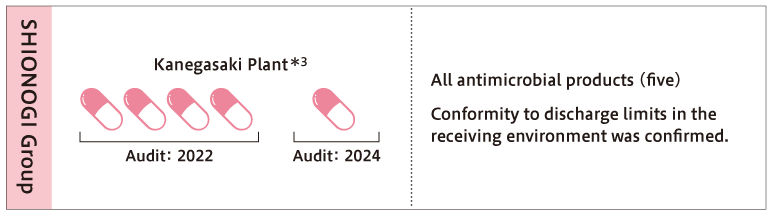
At the Kanegasaki Plant of Shionogi Pharma, a production group company of the SHIONOGI Group, an audit for the “BSI Kitemark™ for Minimized Risk of AMR” was conducted for the manufacturing process of the active pharmaceutical ingredient and formulation of “Cefiderocol,” a treatment for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections, based on the medium- and long-term targets. As a result, in October 2025, the Kanegasaki Plant became the first pharmaceutical manufacturing facility in Japan to obtain this certification.

AMR Audits
Table 1: Audit Targets for Antibiotic Drug Substances Handled by SHIONOGI
In addition to the existing categories of ‘Drug products’ and ‘APIs’, we have added ‘Primary Packaging’ and revised the labeling method accordingly.
APIs of antimicrobials |
Manufacturing site |
Manufacturing process |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
APIs |
Drug products |
Primary packaging |
||
Flomoxef |
SHIONOGI |
● |
● |
● |
Company A(Japan) |
|
● |
● |
|
Cefcapene pivoxil |
SHIONOGI |
● |
● |
● |
Latamoxef |
SHIONOGI |
● |
● |
● |
Doripenem |
SHIONOGI |
● |
● |
● |
Company B(Japan) |
|
● |
● |
|
Cefiderocol |
SHIONOGI |
● |
● |
● |
Company I(Italy) |
● |
|
● |
|
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim |
Company C(Japan) |
|
● |
● |
Company F(India) |
● |
|
|
|
Company G(India) |
● |
|
||
Metronidazole |
Company D(Japan) |
|
● |
● |
Company H(Italy) |
● |
|
|
|
Company E has been removed as it is no longer a supplier to SHIONOGI.
*1 AMRIA (External link)
At the Davos meeting held in September 2016, we signed the “AMR Industry Roadmap” together with 12 leading companies. The signatory companies proactively manage their own groups and contractors, establish a roadmap for AMR countermeasures, and provide management methods for environmental emissions to all antibiotic manufacturers to suppress AMR occurrence. This activity has now developed into the AMRIA, which includes many companies that handle antibiotics.

*2 Antibiotic Manufacturing Standard (External link)
In May 2025, the Standard was revised to add “primary packaging” to the previously targeted pharmaceutical and formulation processes. Accordingly, when planning AMR audits from fiscal year 2026 onward, suppliers entrusted only with primary packaging will also be audit targets.
Table 2: Supplier Audit Results (Results up to FY2024)
| Supplier | Management system | Wastewater management | Solid waste material management | Conformity to discharge limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Company B | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Company C | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Company D | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | △ |
| Company F | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Company G | 〇 | △ | 〇 | △ |
| Company H | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Company I | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
Company E has been removed as it is no longer a supplier to SHIONOGI.
○: Conforms to the “Standard”
△: Partially non-conforming to the “Standard”; corrective actions are being implemented
×: Multiple non-conformities with the “Standard”; corrective actions are being implemented
Efforts to Control and Manage Antibiotic Release
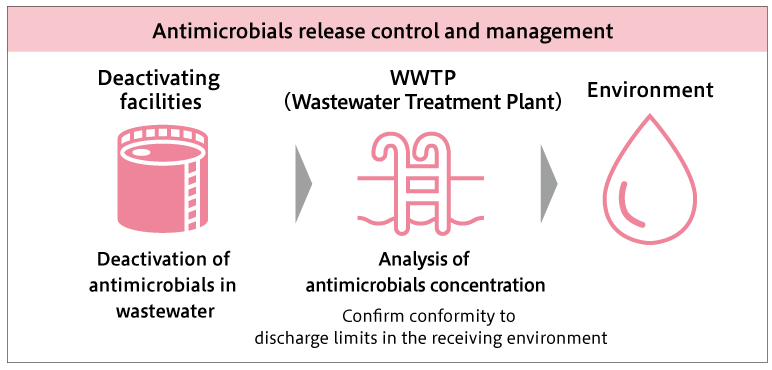
At the Kanegasaki Plant, SHIONOGI’s flagship antibiotic manufacturing facility, wastewater generated during the manufacturing process is treated for antibiotic inactivation in each manufacturing building as part of efforts to control and manage emissions. The treated wastewater is discharged via the wastewater treatment facility at the site.
In addition, the concentration of antibiotics in the wastewater discharged from the site is evaluated annually based on the AMRIA Standard. For all five antibiotic products currently manufactured at the Kanegasaki Plant, the concentration in the wastewater is below the “environmental emission standard value”*4, indicating that there is no impact when released into the natural environment. Concentration evaluation is conducted using direct measurement by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass balance calculation based on the manufacturing volume and wastewater volume.
If any abnormality is detected, the wastewater is temporarily diverted to an emergency storage tank and is collected and treated to prevent discharge into the natural environment.
External specialists collect and incinerate the solid waste generated from the antibiotic manufacturing process, ensuring that antibiotics are not released into the environment via solid waste.
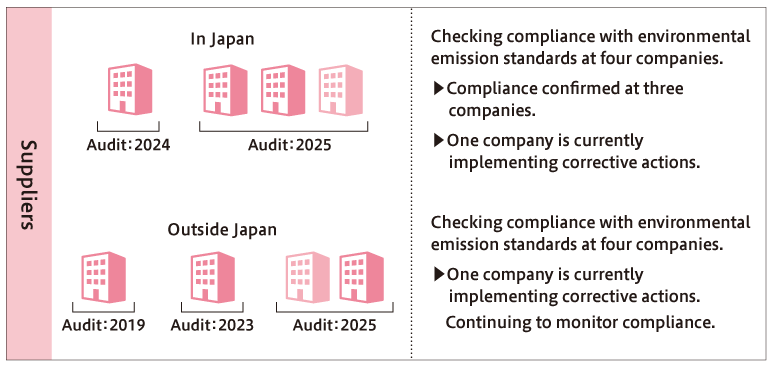
For antibiotics manufactured by suppliers, AMR audits have confirmed compliance with environmental emission standards for three out of four products manufactured by four domestic companies. Corrective actions are being implemented for one product at one company where compliance was not confirmed. Similarly, for four products manufactured by four overseas companies, compliance has been confirmed for three products at three companies, and corrective actions are underway for one product at one company. SHIONOGI will continue to conduct AMR audits for domestic and overseas suppliers and verify compliance with environmental emission standards.
Panel Participation in “One Health—AMR and the Environment”
In June 2024, Gareth Morgan (Global Head, Portfolio Management and AMR Policy) of Shionogi Inc. participated as a panelist in the BSI-sponsored webinar event “One Health—AMR and the Environment.” He explained SHIONOGI’s efforts to control and manage the release of antibiotics from its manufacturing plants and the status of AMR audits for related suppliers to an audience of antibiotic manufacturers and suppliers.
“One Health—AMR and the Environment” (External link)