Chemical Substances
Initiatives for Chemical Substance Management
PRTR
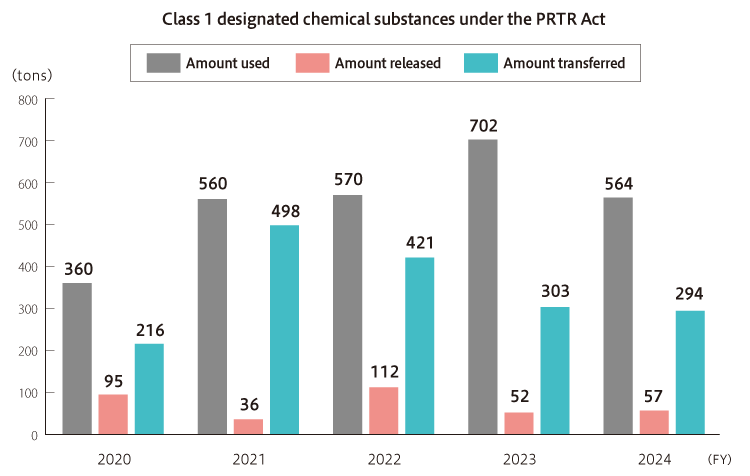
Substances Reported under the PRTR Act (Unit: kg)
| Substance name*1 | Usage amount | Amount released | Amount transferred | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Drainage (public waters) |
Soil | Outside operating sites | Sewers | ||
| N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone | 55,132 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 55,110 | 0 |
| Chloroform | 8,598 | 307 | 0 | 0 | 8,290 | 0 |
| Dichloromethane (methylene chloride) | 153,957 | 53,204 | 5 | 0 | 85,771 | 0 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 152,855 | 2,761 | 0 | 0 | 85,839 | 0 |
| Toluene | 1,745 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 1,727 | 0 |
| Hexane | 6,437 | 365 | 0 | 0 | 6,072 | 0 |
| Carbon disulfide | 3,783 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 3,745 | 0 |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | 10,605 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 5,577 | 0 |
| Tributylamine | 4,855 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pyridine | 11,312 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9,302 | 0 |
| 4-Methyl-2-pentanone (methyl isobutyl ketone) | 141,099 | 176 | 0 | 0 | 26,577 | 0 |
| N,N-Dimethylacetamide | 12,990 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5,615 | 0 |
| Acetic anhydride | 1,089 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| G. total | 564,457 | 56,951 | 5 | 0 | 293,629 | 0 |
Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)
PCBs are synthetic, mainly oily chemical substances. It has been reported that PCBs cause various symptoms when they accumulate in the bodies of living organisms. PCBs are resistant to decomposition in the environment and soluble in fat; therefore, they tend to accumulate in living organisms through the food chain, raising concerns about global-scale environmental pollution. PCBs were previously used in items such as condensers, transformers, and fluorescent light ballasts, and strict management is required for waste and equipment containing PCBs.
SHIONOGI appoints managers for each organization and site to properly manage the PCB-containing equipment. In accordance with the Act on Special Measures concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes (PCB Special Measures Act), we have gradually proceeded with the proper disposal of PCB-containing equipment and completed the disposal of all equipment containing high concentrations of PCBs in our buildings and premises by FY2022. We continue to take steps to complete the disposal of equipment containing low PCB concentrations by March 31, 2027, the deadline set forth in the PCB Special Measures Act.
Fluorocarbons
Environmental and Safety Considerations in Chemical Processes
In the development of manufacturing and testing methods for pharmaceuticals and candidate compounds, and in the design stage of related equipment, SHIONOGI conducts preliminary assessments of the safety of chemical substances and the risks of reactions and incompatibilities. We also examine manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency in terms of waste reduction and energy conservation during production.
For details on the management of environmental release of antimicrobials, please refer to the AMR section.

